Dirt Doesn't Burn: Fire Resistant Home Design
As wildfires and extreme weather become more frequent, fire safety has become essential. Choosing fire-resistant construction is one of the smartest ways to protect your home and your peace of mind. If you're looking to build a fire resistant home, compressed earth blocks are a strong choice. They function as structural masonry and, unlike wood or synthetic materials, they do not burn. This is because earth blocks are made from clean, compacted dirt without organic matter, which makes them naturally resistant to fire.
Achieving Fire Resistance with Earth Blocks -
- Naturally Non-Combustible: Made from inorganic soil, sand, and stabilizers like lime or cement, earth blocks are naturally fireproof and ideal for fire-prone areas. Unlike wood, they don’t catch fire, offering superior protection.
- High Heat Resistance: Earth blocks are great at handling high temperatures during a fire, keeping their structure intact much longer than wood or other materials. They've been tested to meet international fire standards, though performance can vary depending on the exact mix used.
- Built for Safety: Homes made with earth blocks can meet strict fire safety codes, but it's always important to ensure your design complies with local regulations. With the right engineering, these homes offer excellent protection against fire.

Fire Resistance Test References for Earthen Walls -
Lab tests following standards like ISO 834‑1 and ASTM E119 show that properly designed earthen walls can offer excellent fire resistance. Fire performance ultimately depends on factors like block mix, stabilizers, and wall thickness, so it’s important to review testing data that reflects your specific materials.
ISO Fire Testing on Compressed Earth Block Walls - Buson et al. (2013) tested soil-cement and Kraftterra CEB walls using the ISO 834-1 fire curve, achieving 120 minutes of fire resistance without failure. The paper also references earlier tests by Byrne (1982), where CEB walls endured four hours of fire exposure with only minimal deflection.
Cob & Adobe Fire Rating Equivalency Analysis - Originally published by the Cob Research Institute (2019), this FEMA-backed analysis shows how adobe and cob walls meet or exceed standards like ASTM E119, AS 1530, and EN 1363, offering a close comparison to compressed earth block performance.
UC Davis CITRIS Wildfire Simulation – Earth blocks subjected to a blowtorch with temperatures above 3,000°F showed minimal surface damage, while wood blocks charred and failed quickly.
These examples represent a small selection of available fire-resistance tests. Additional studies have demonstrated similar performance outcomes, depending on material composition and construction methods.

How fire-resistant are compressed earth blocks (CEBs) in real-world scenarios?
How fire-resistant are compressed earth blocks (CEBs) in real-world scenarios?
CEBs are highly fire-resistant and have been tested to withstand extreme temperatures. In fact, a 10-inch-thick earth block wall was tested to ISO standards and withstood fire for 120 minutes without damage. You can read more about it in the full article here.
Do compressed earth blocks (CEBs) lose strength in a fire, like concrete?
Do compressed earth blocks (CEBs) lose strength in a fire, like concrete?
While concrete can lose strength in high heat due to moisture evaporation and cracking or flaking, CEBs are more heat-resistant. Earth materials like CEBs and adobe have low thermal conductivity and don’t undergo the same chemical changes as concrete. They maintain their structural integrity longer in fire conditions, making them a more resilient choice compared to concrete and wood.
How does adding cement stabilization, affect the fire resistance of CEBs?
How does adding cement stabilization, affect the fire resistance of CEBs?
Adding a low percentage of cement to CEBs improves their durability and structural integrity in harsh conditions, like freeze-thaw cycles.
At this level, the cement content is low enough that the blocks should retain much of their fire resistance
and are less likely to crack or break apart compared to high-cement materials like concrete.
Will adding a finish to my CEB walls affect their fire resistance?
Will adding a finish to my CEB walls affect their fire resistance?
CEB walls are already great at resisting fire, but the type of finish you use can make a difference. If you use a non-breathable finish, moisture can get trapped inside the walls, increasing the risk of spalling (breaking or flaking) during a fire. To avoid this, it’s best to use breathable finishes like lime plaster, which allow moisture to escape while still protecting the walls.
Comprehensive Fire Resistant Home Strategies -
Earth block walls are naturally fireproof, but pairing them with fire resistant roofing, smart venting, and defensible space around your home takes your fire protection to the next level. Here’s how these strategies can help keep your home safe from wildfires and other fire risks.
Defensible Space: Maintain a defensible space around your home by clearing away combustible vegetation and debris from the roof and gutters.
- Maintain a 30–100 ft. buffer zone around the home (based on local guidelines).
- Remove dead plants, dry leaves, and combustible debris from the yard, roof, and gutters.
- Plant fire-resistant vegetation like succulents or low-growing, drought-tolerant plants.
- Use hardscaping (gravel, stone, patios) as firebreaks to prevent fire spread.
Fire Resistant Roof Materials: Choosing the right fire-resistant roofing materials is essential for preventing embers from igniting the roof, which is one of the most vulnerable parts of any home in a wildfire.
- Metal Roofing: Non-combustible, durable, and fire-resistant (steel, aluminum, copper).
- Clay or Concrete Tiles: Heavy, non-combustible, flame, and ember resistant.
- Slate Roofing: Natural stone with strong fireproof qualities.
- Class A Fire-Rated Asphalt Shingles: Fire-treated, affordable, and effective.
- Fiber Cement Shingles: Lightweight, non-combustible, mimics wood or stone, fire-resistant.
- Fire-Resistant Eaves, Soffits, Gutters, and Flashing: Use non-combustible metal and gutter guards to block ember accumulation.
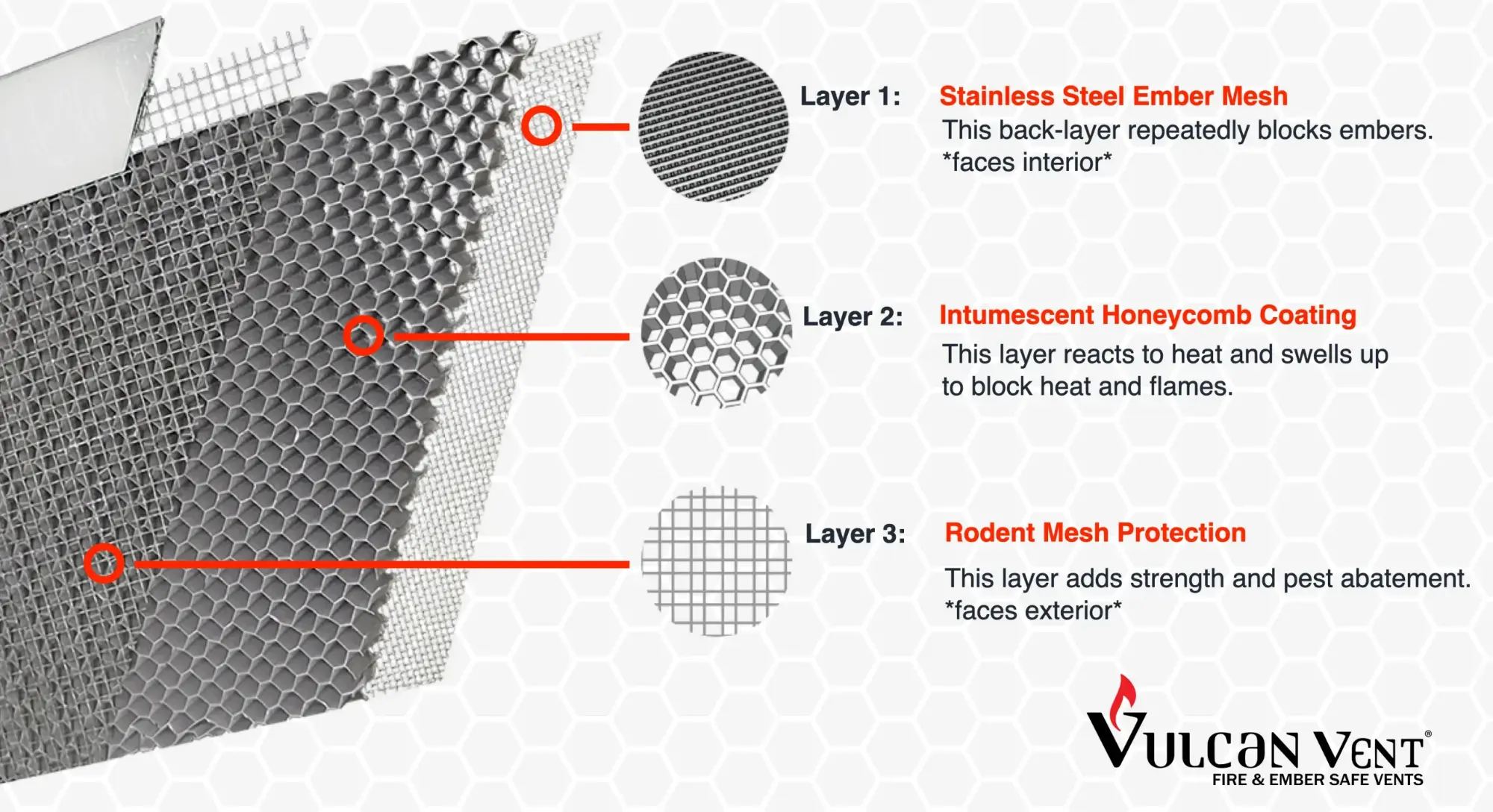 Vulcan Vent Diagram
Vulcan Vent DiagramThe design of your roof can significantly impact the fire resistance of your home. Choosing venting strategies and roof assembly methods that limit ember penetration is crucial.
Vented Roof Strategies:
-
Ember-resistant vents: Use non-combustible fine mesh screens (1/8 inch) to block embers while allowing airflow. (Cons:
can clog with dust and debris without regular maintenance and may reduce ventilation efficiency).
- Fire-Rated Vents: Install wildfire-resistant vents like Brandguard or Vulcan, with heat-activated coatings that seal openings. (Cons: are more expensive than standard vents due to their specialized fire protection features).
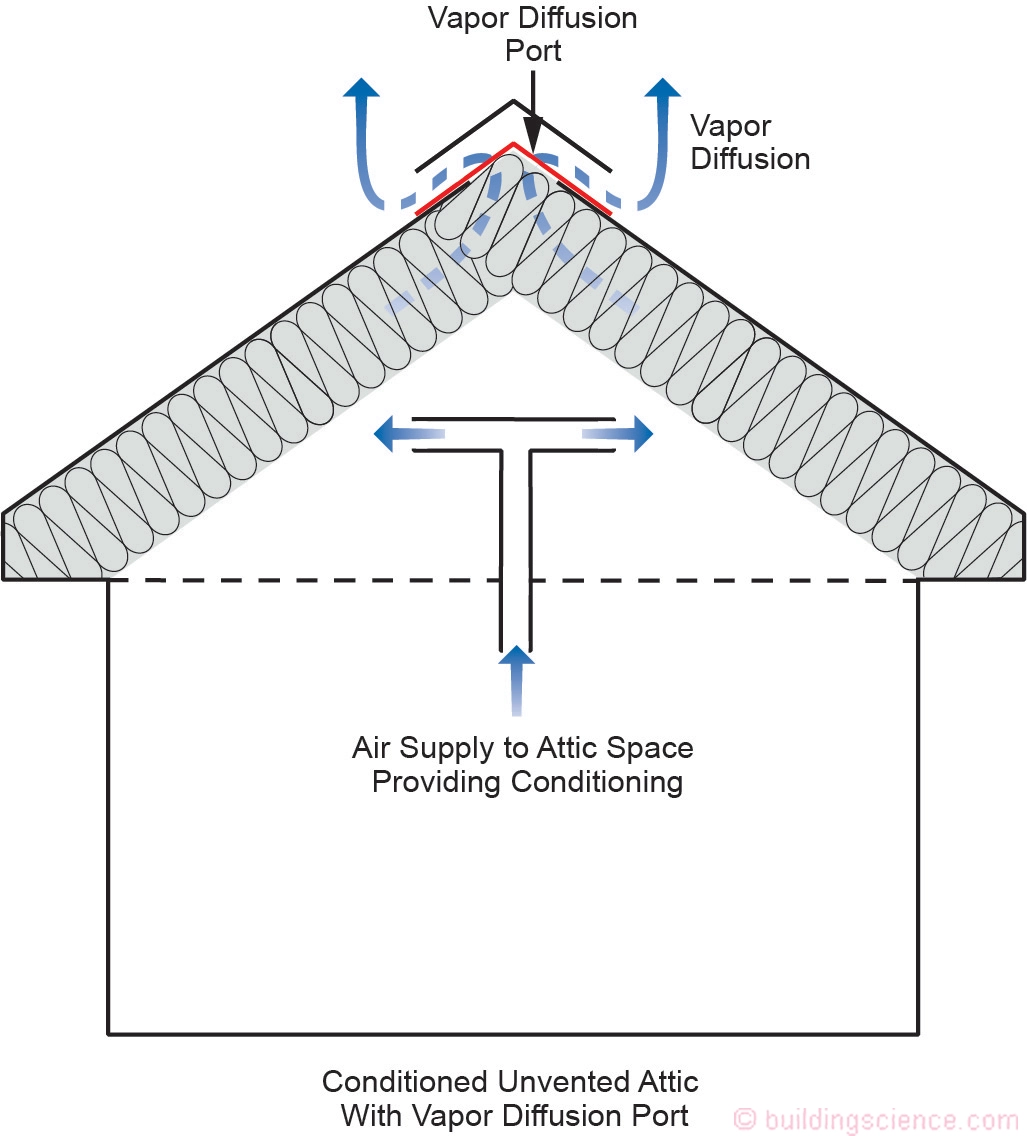 Unvented Attic with Air-permeable insulation (buildingscience.com)
Unvented Attic with Air-permeable insulation (buildingscience.com)Non-Vented Roof Strategies:
- Sealed, Non-Vented Roof Design: Eliminates roof vents, reducing ember entry points. Options include spray foam, rigid foam, or hybrid assemblies with air-impermeable and air-permeable insulation, applied above or below the roof deck. Climate and mechanical system considerations are crucial to avoid moisture and ventilation problems.
- Vapor Vents for a Greener Alternative: Combining vapor ports with natural insulation is a complex issue that requires careful consideration of climate, building design, and mechanical systems.
Green Roofs: A Natural Layer of Fire Resistance
For the green-living enthusiasts, green roofs, covered with vegetation,
can provide an extra layer of fire resistance by acting as a natural
fire barrier. The plants and soil help shield your roof from embers and
radiant heat.
Fire Resistant Windows and Doors: Windows and doors are also vulnerable points in a wildfire. Protecting these areas is important for the overall fire resistance of your home.
- Tempered Glass Windows: Use double or triple-pane tempered glass for heat and fire resistance.
- Fire-Rated Doors: Install solid core or fire-rated metal doors to block fire entry.
- Shutters or Fire Curtains: Add non-combustible shutters or fire-rated curtains for window protection during fires.
Air Sealing for Fire Resistant Home Design: Air sealing plays a key role in enhancing the fire resistance of your home by closing off gaps where embers, smoke, and heat can infiltrate. Proper air sealing strengthens your home’s defense during wildfire events.
- Seal Gaps: Seal windows, doors, and openings with fire-resistant materials to block embers.
- Roof and Wall Joints: Seal roof-to-wall areas to prevent ember entry.
- Weather Stripping and Caulking: Use high-quality, fire-rated weather stripping and caulking for a continuous seal.
Air sealing not only improves energy efficiency but also adds an extra layer of fire protection by reducing vulnerable spots where fire can enter the home.

Build a Fire Resistant Home for Lasting Protection
Want to learn more about building a fire resistant home using earth blocks? Contact us today to explore how earth block construction, combined with fire-resistant design strategies, can help you build a home that’s both beautiful and resilient.